/ Story: Kor Lordkam / English version: Bob Pitakwong /
/ Infographic Designer: Chittawat /
In this presentation, we take a look at war memorials across Southeast Asia, ones that inspire people to be cognizant of the turbulent past, live in the present and look to the future.

Wars have the potential to bring destruction, death and losses, not to mention physical and mental injuries. They have long-lasting impacts on the social and economic fabric of countries. Soldiers who fought the battle knew only too well what it meant to suffer from a psychological trauma. So did civilians who accounted for the majority of war-time casualties.
There is no denying that violent conflicts bring painful experiences hard to be reconciled with. In memory of the hardships and tribulations, monuments are erected. Some are built in remembrance of those who died heroic deaths. Others serve as grim reminders of the terrible things that happened. Sadly, life that’s lost cannot be brought back again.
The countries of Southeast Asia are no strangers to tragic events of the past. Each one of them has a sense of history and heritage to pass on to its next generations. That’s reason enough to commemorate the struggles, freedoms and notable events that have come to define a country’s distinct character.
The Rizal Monument
Manila, the Philippines
Erected: 1913
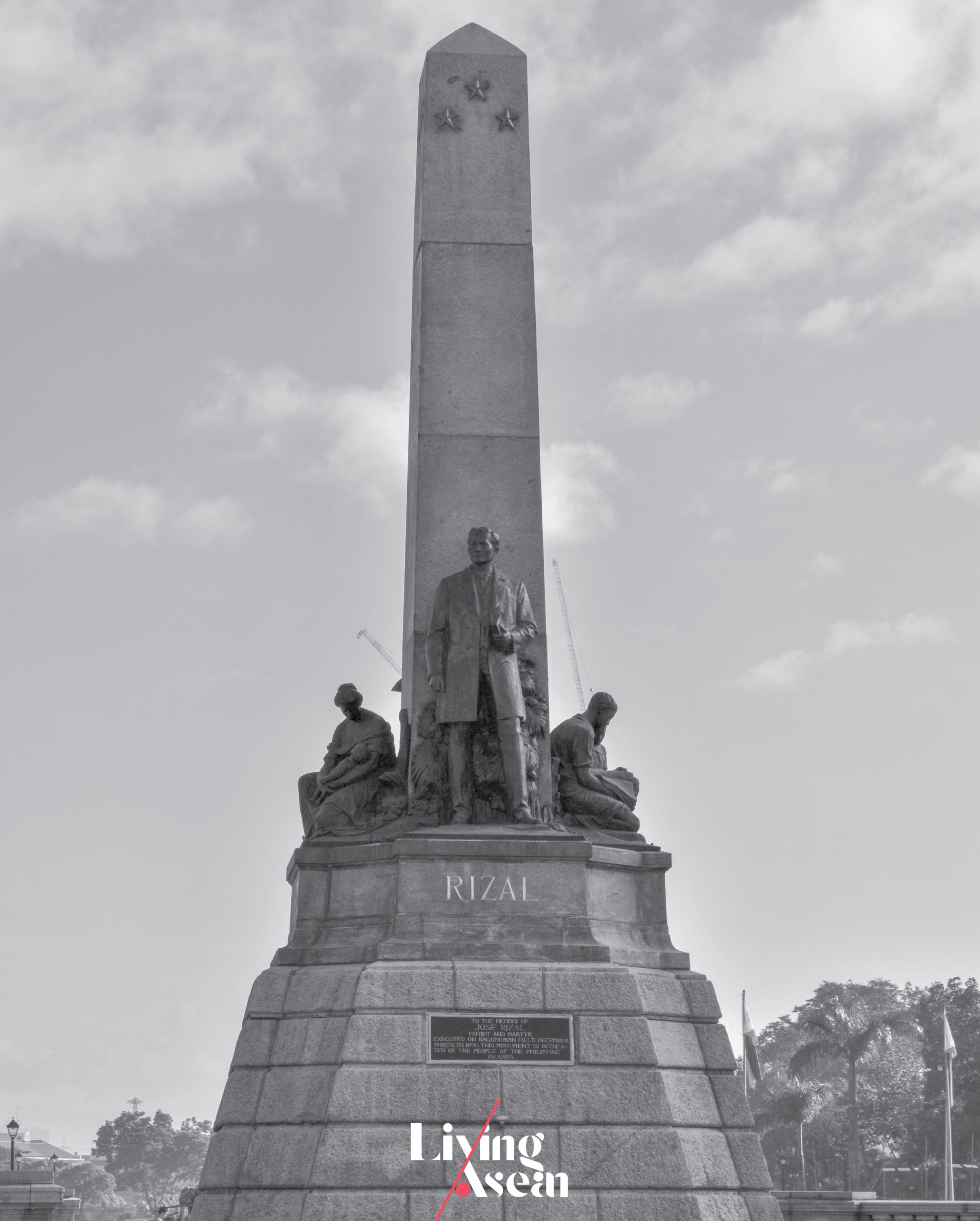

The Rizal Monument is a memorial to José Rizal, the Philippine national hero, writer and leader of a reform movement. He was widely recognized for his writings that centered on liberal and progressive ideas, freedom and individual rights of the Filipino people.
An advocate of political reform in the Philippines, he was arrested and brought to trial for the crime of rebellion after the Philippine Revolution broke out. He was found guilty and eventually executed by the Spanish colonial administration in 1896. The Spanish-American War brought Spain’s rule on the islands to an end in 1898, only to be followed by the Philippine-American War between 1899 and 1902.
Memorials in honor of José Rizal were erected in several places, the most well-known of which being the Rizal Monument built in 1913. It’s situated at Rizal Park, also known as Luneta Park, one of the most famous landmarks in Manila.
Reference: [1] [2]
The Rangoon Memorial
Yangon, Myanmar
Erected: 1951
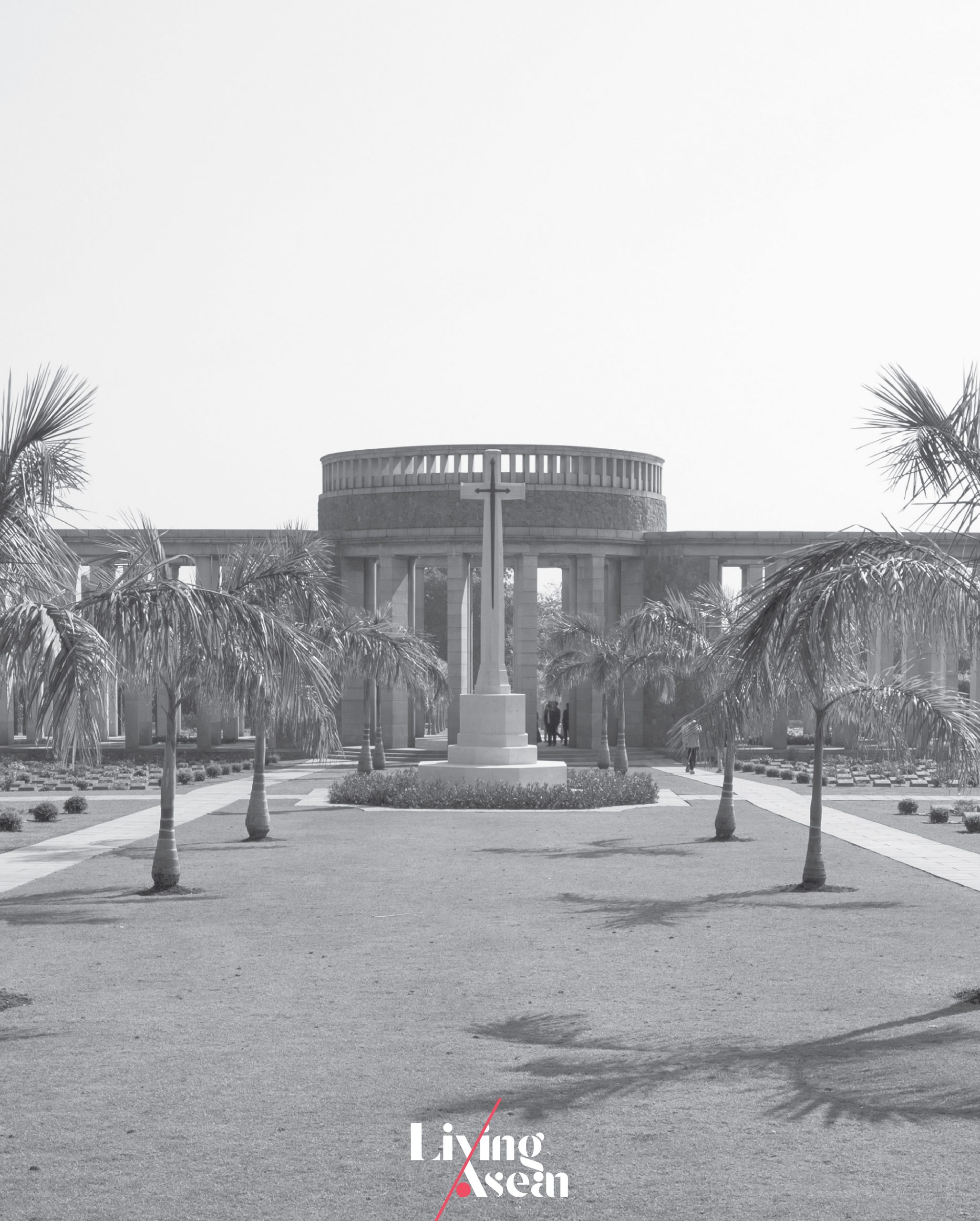

The Rangoon Memorial is part of the Taukkyan War Cemetery, the largest of the three battlefield cemeteries in Myanmar. It’s located about an hour’s drive from the Yangon city proper.
More than 27,000 names of men of the Commonwealth land forces who died in military operations across Burma (now Myanmar) are displayed here. The Taukkyan War Cemetery is a Commonwealth burial ground for more than 6,300 soldiers who perished during the Second World War, of whom only 5,500 men could be positively identified.
Reference: [1] [2]
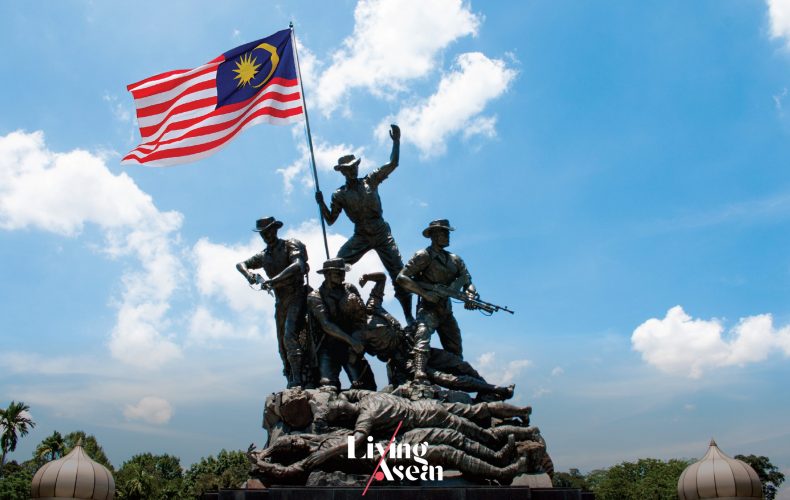
The Tugu Negara
Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Opened: 1966
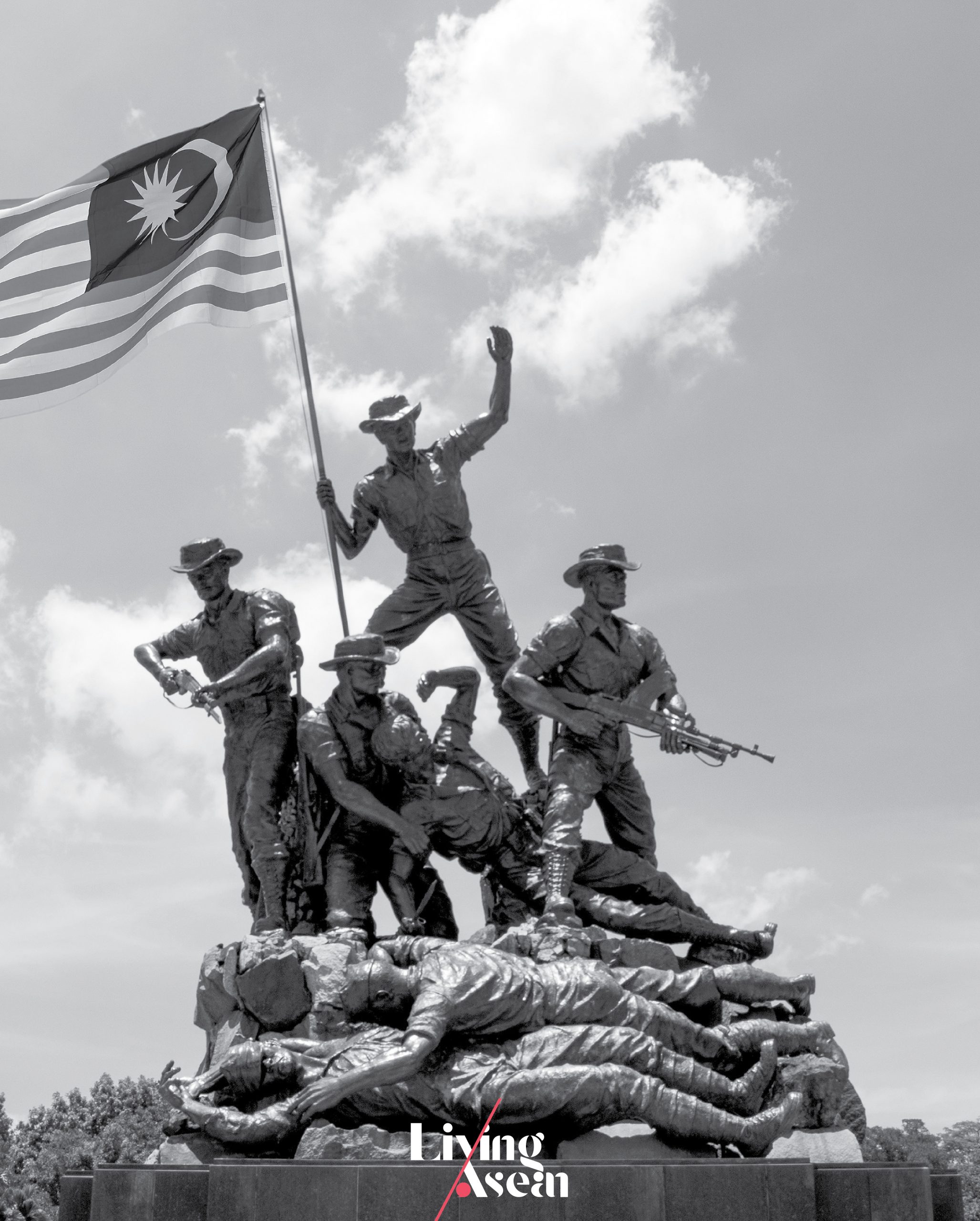

The Tugu Negara, or National Monument, is a 15-meter-tall bronze sculpture in the center of Kuala Lumpur. Designed by Austrian-American artist Felix de Weldon, it’s a memorial to those who died fighting for freedom. The Tugu Negara features a sculpture of seven human figures representing seven key attributes of Malaysia as a nation, namely, courage, sacrifice, leadership, suffering, strength, unity and vigilance.
Taken as a whole, it’s a reminder of the struggles against the Japanese occupation during World War II and the loss of many lives during the Malayan Emergency, guerrilla warfare fought in then British Malaya between communist pro-independence fighters and the combined forces of the Federation of Malaya, the British Empire and the Commonwealth from 1948 to 1960.
Reference: [1]
The Civilian War Memorial
Singapore
Opened: 1967
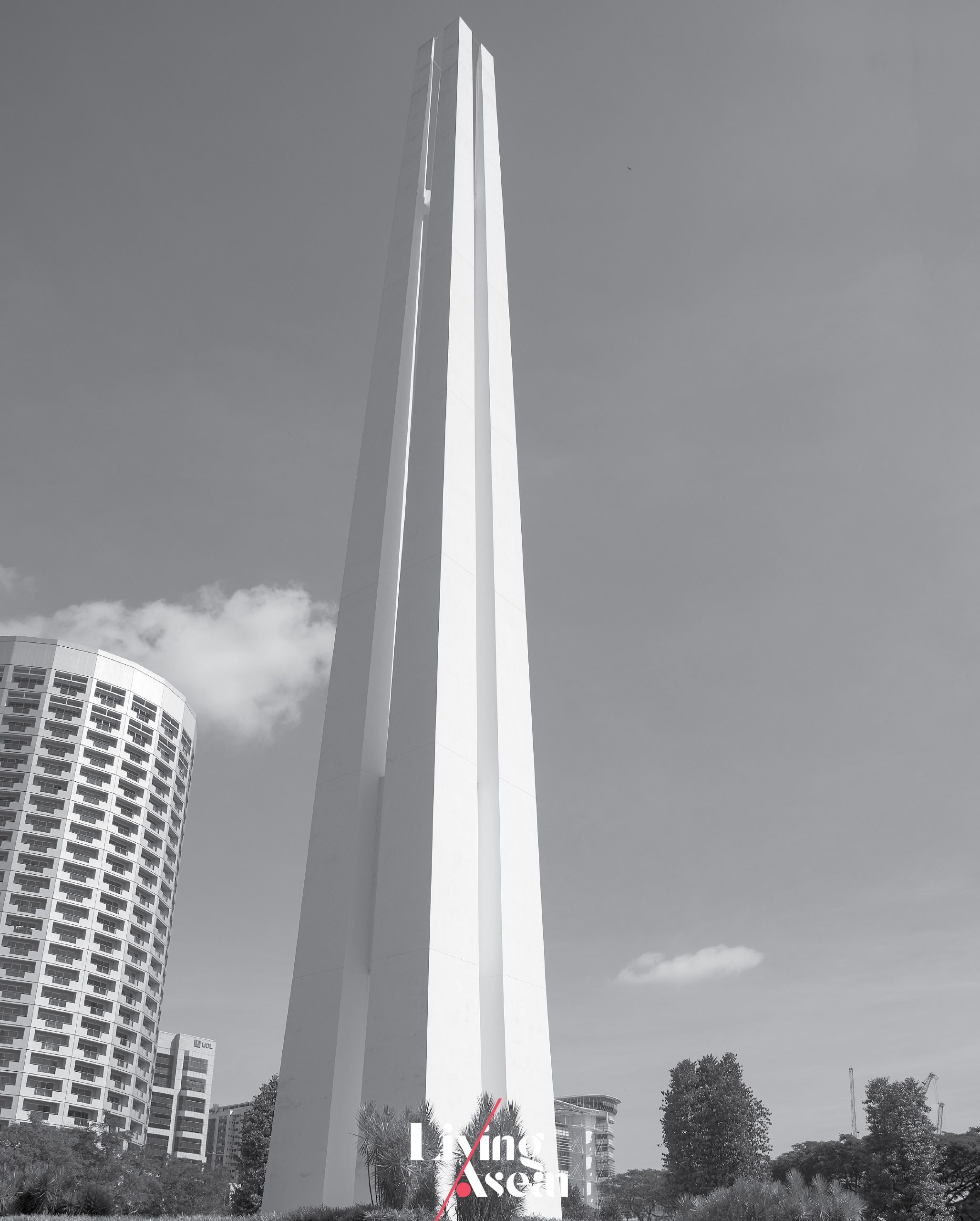

The Civilian War Memorial is a heritage landmark dedicated to civilians who died during the Japanese occupation of Singapore in World War II from 1942 to 1945. It’s the brainchild of Singaporean designers from Swan and Maclaren Architects, a homegrown architectural and industrial design firm.
The memorial sculpture standing 68 meters tall consists of four pillars representative of people of four races, namely Malay, Chinese, Indian and Eurasian, who perished during the war. The number of civilian victims taken away and executed by the Japanese occupation forces has been unknown, but the Singapore Chinese Chamber of Commerce reported a figure of 40,000 deaths.
Reference: [1] [2]
The Patuxai
Vientiane, Laos PDR
Completed: 1968
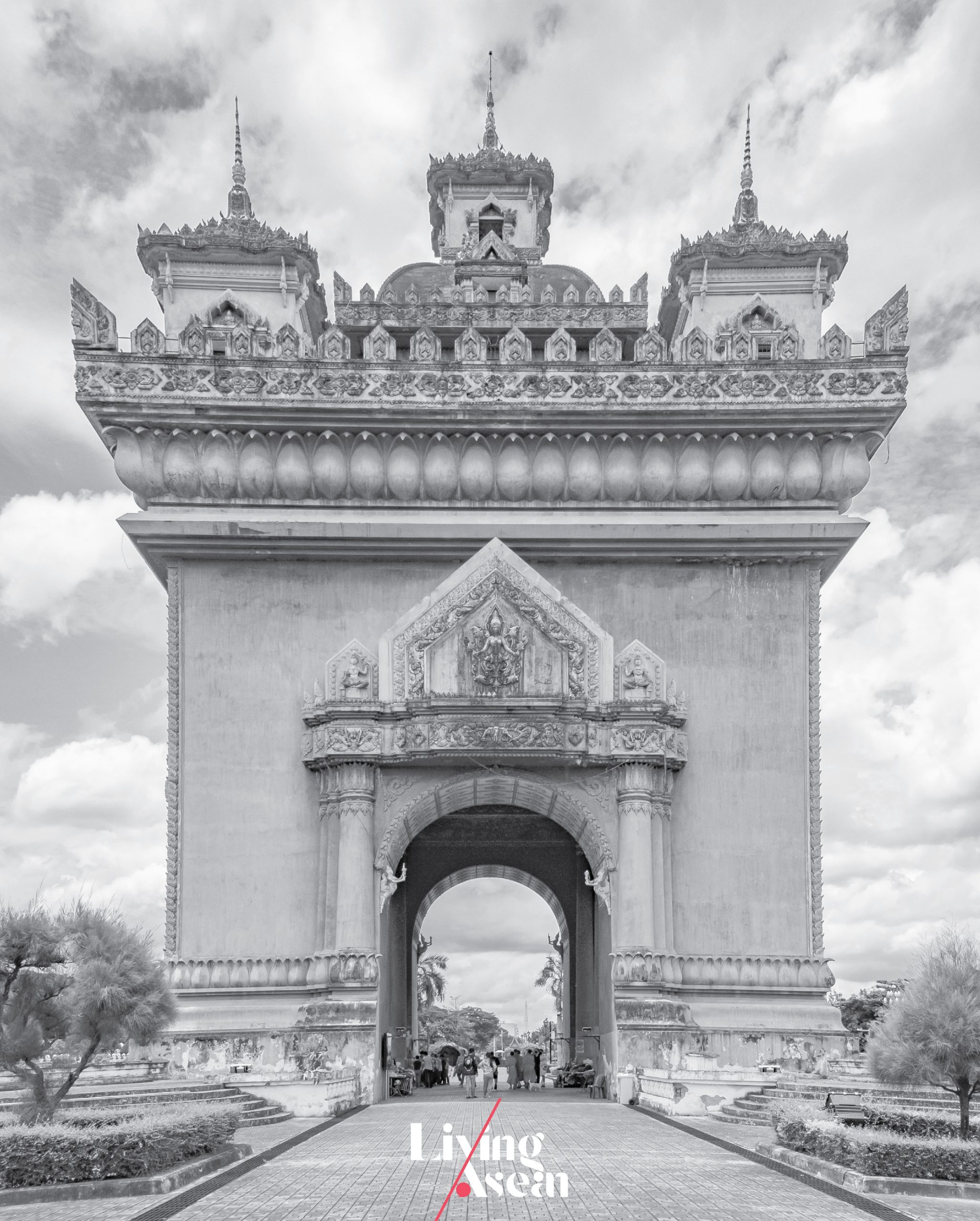

The Patuxai, literally Gate of Victory, is erected in remembrance of those who died fighting to protect their fatherland during World War II. It’s also a memorial to the struggles that resulted in the country gaining independence from French colonial rule in 1949. It’s modeled on the Arc de Triomphe in Paris, except for the decorating sculptures that convey a great deal about the culture and belief systems unique to Laos.
Together they form the basis of a mix of religions, namely Buddhism, Brahmanism and Hinduism that’s evident in the figures of deities and mythical creatures from ancient literature. They include Kinnaree, the female bird with a human head; and Erawan, the three-headed elephant. The Patuxai is a memorial landmark in the center of Vientiane, the capital of Laos PDR.
Reference: [1] [2]
Monumen Nasional (Monas)
Jakarta, Indonesia
Opened: 1975
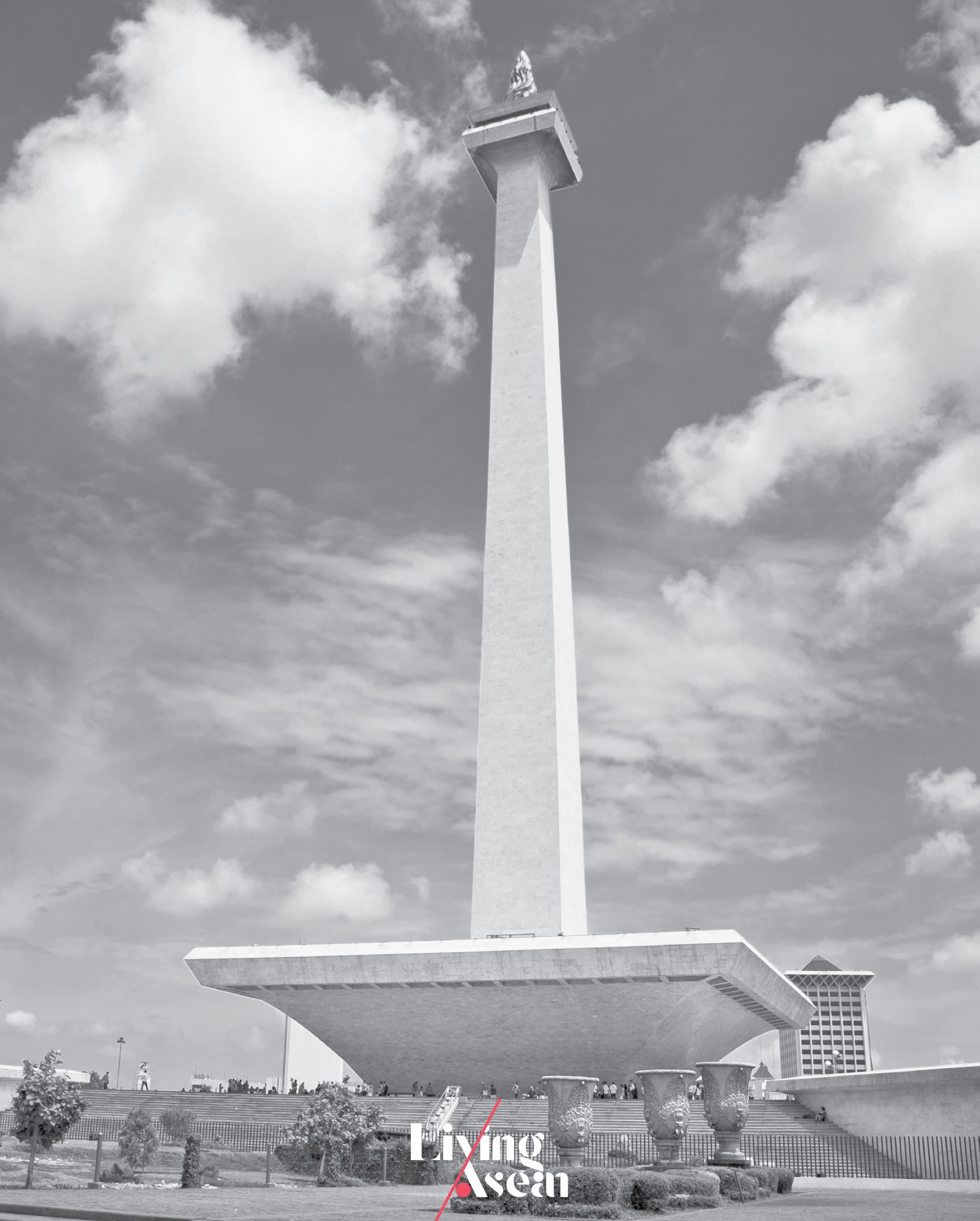

The National Monument, also known as Monumen Nasional, or Monas, commemorates the struggle for Indonesian independence. It stands as a testimony to the hardships and the fight for freedom from the Dutch who ruled Indonesia from 1816 to 1941, only to be followed by the Japanese occupation which ended in 1945.
Indonesian architect Friedrich Silaban submitted his design for the National Monument in 1955, but the project was further refined and eventually completed by another architect, R.M. Soedarsono.
The obelisk (square stone pillar) carries the torch of Indonesian independence at the top decorated with bronze and gold. It stands in the middle of 80-hectare parkland that’s part of Merdeka Square in the center of Jakarta.
Reference: [1] [2]
The Son My Memorial
Quang Ngai, Vietnam
Erected: 1978
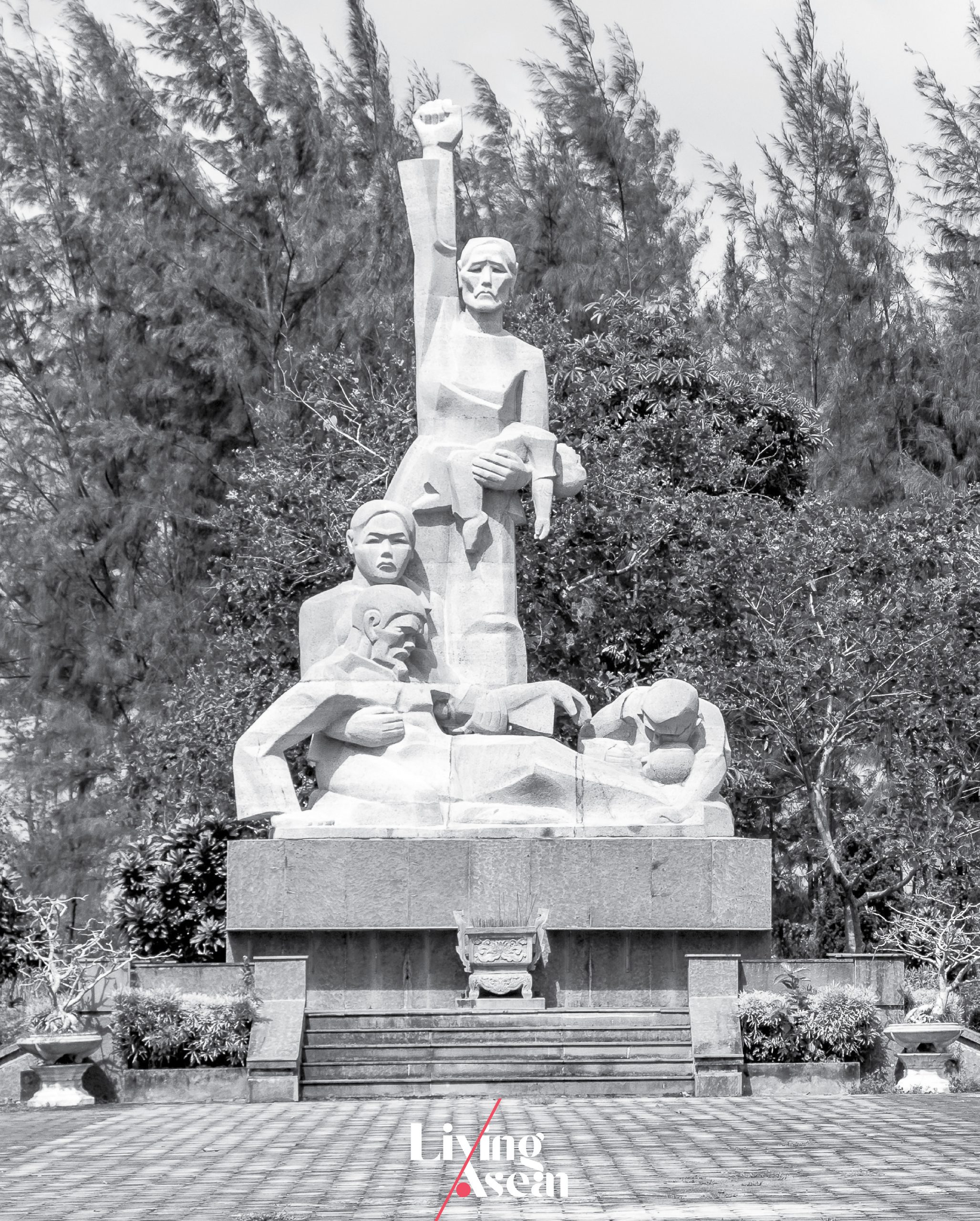

The Son My Memorial is dedicated to victims of the My Lai Massacre that took place at Son My village, Quang Ngai Province, formerly South Vietnam. The indiscriminate killing of civilians by United States Army personnel happened at the height of the Vietnam War in 1968. The GI’s arrived in the area expecting to engage the National Liberation Front (NLF), but ended up killing innocent civilians instead.
As fighting escalated in the area, it was estimated that more than 500 lives were lost. The world reacted in shock and horror. The Son My Memorial is depicted as a time of unwavering resolve in the face of tragedy and great suffering. Now the village is home to a museum and paraphernalia that people keep as reminders of the tragic event.
Reference: [1] [2] [3]
The Choeung Ek Genocidal Center
Phnom Penh, Cambodia
Established: 1988
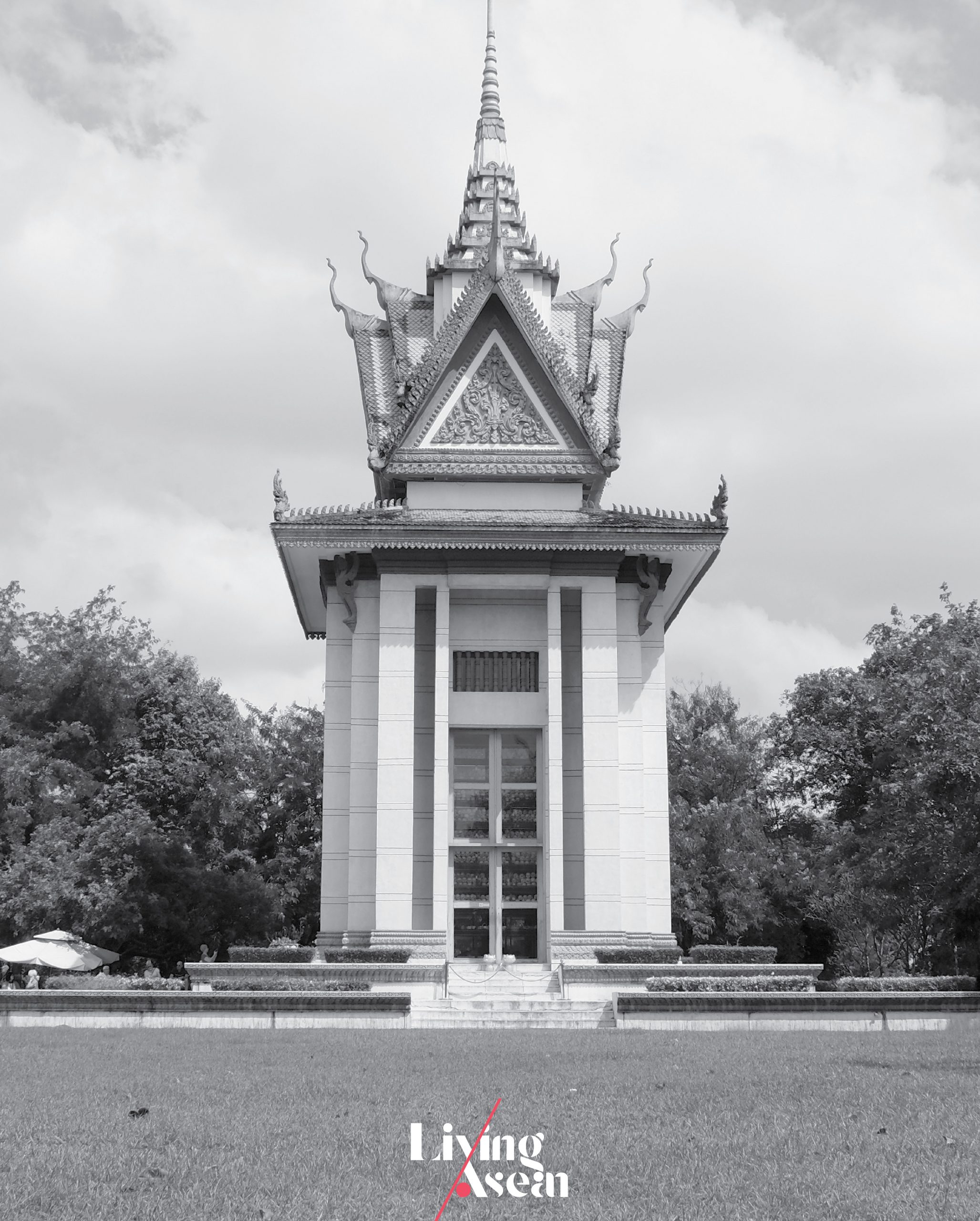

The Choeung Ek Genocidal Center is located 15 kilometers from Phnom Penh, the capital of Cambodia. Formerly referred to as the Killing Fields of Choeung Ek, it’s the best-known among a few hundred sites that communist Khmer Rouge forces used to exterminate their adversaries during internal conflicts that took place between 1975 and 1979.
It was estimated that more than 20,000 people were killed and buried in mass graves at this site alone. Approximately two million lives were lost at the hands of the Khmer Rouge countrywide. Choeung Ek is now home to a memorial museum dedicated to victims of the Khmer Rouge.
It’s a tall building with multi-tiered roof design symbolic of Buddhist architecture. Inside, piles of human skulls and bones are on display as a grim historical reminder. Outside, the surrounding landscape calls attention to years the country was turmoil.
Reference: [1] [2]
The Hellfire Pass
Kanchanaburi, Thailand
Opened: 1998
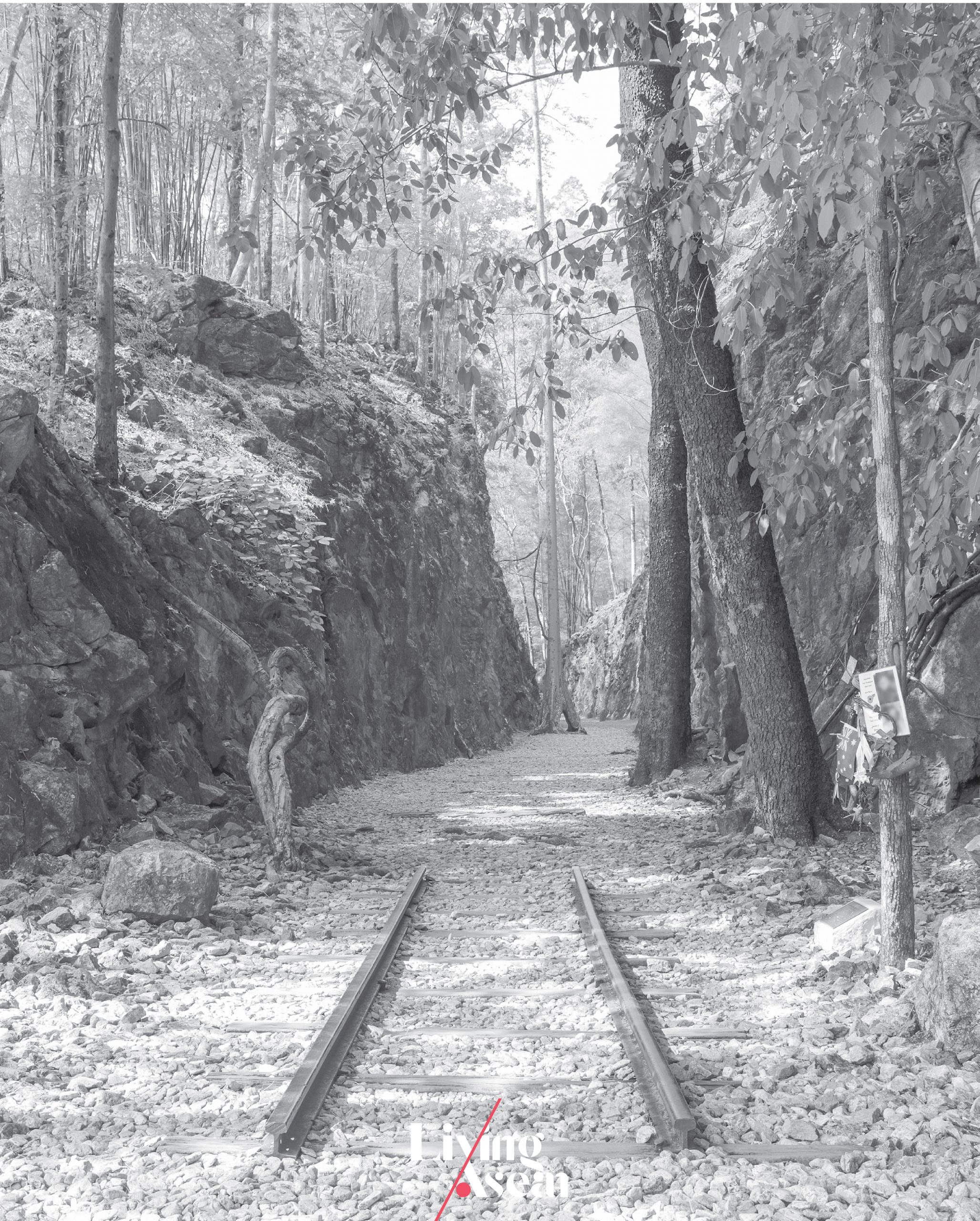

The Hellfire Pass, or Chong Khao Khat in Thai, is a preserved historic site located in mountainous terrain in the western part of Kanchanaburi bordering on Myanmar. It’s home to the infamous railway cutting site on the former Burma Railway line built during World War II by forced labor including allied prisoners of war from several countries.
About 12,800 allied prisoners died of malnutrition and disease along with another 90,000 Asians who perished building the so-called “Death Railway”. The Hellfire Pass that was the most difficult section of the then Siam-Burma railway line has been preserved in memory of the allied prisoners and forced labor working under harsh conditions cutting through rocks under torchlights at night, a sight conjuring up the image of fires of hell.
Reference: [1] [2]
You may also like…
 8 ASEAN Countries Fare Badly on Corruption Index
8 ASEAN Countries Fare Badly on Corruption Index
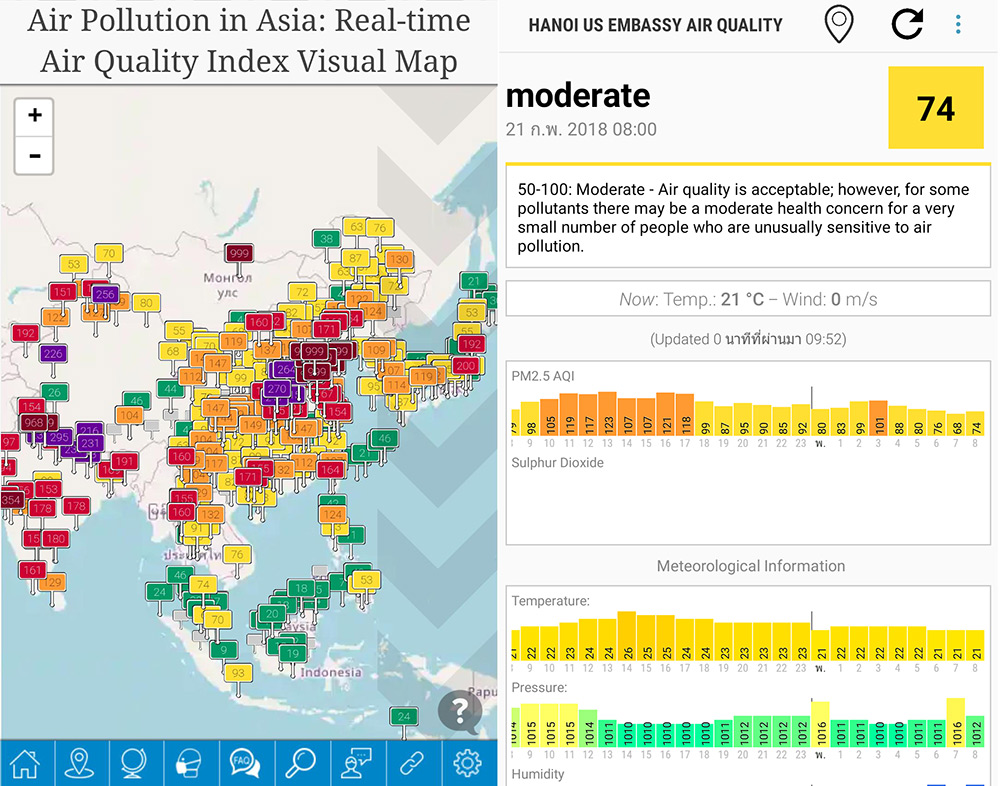
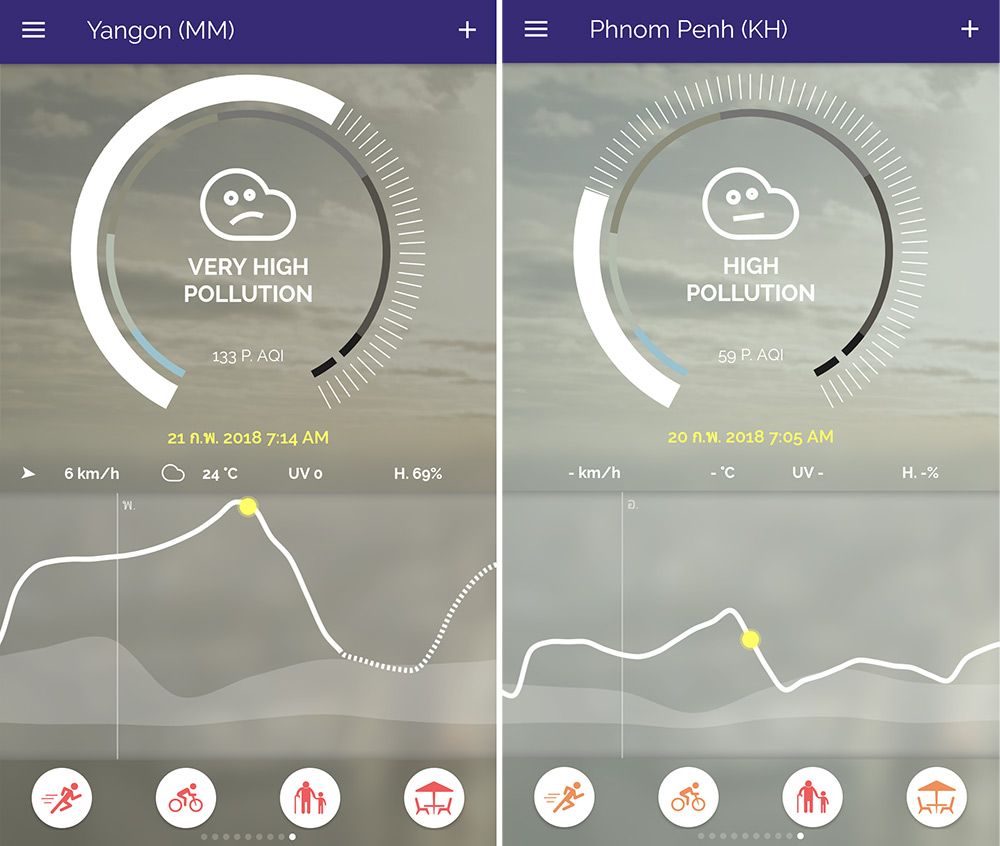
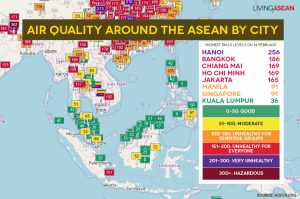
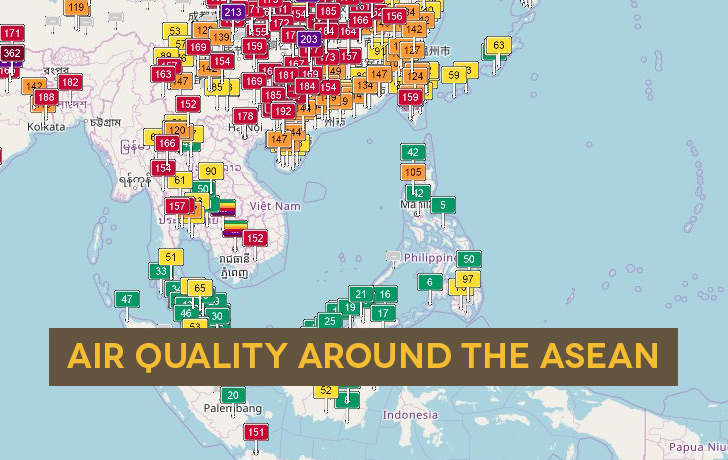
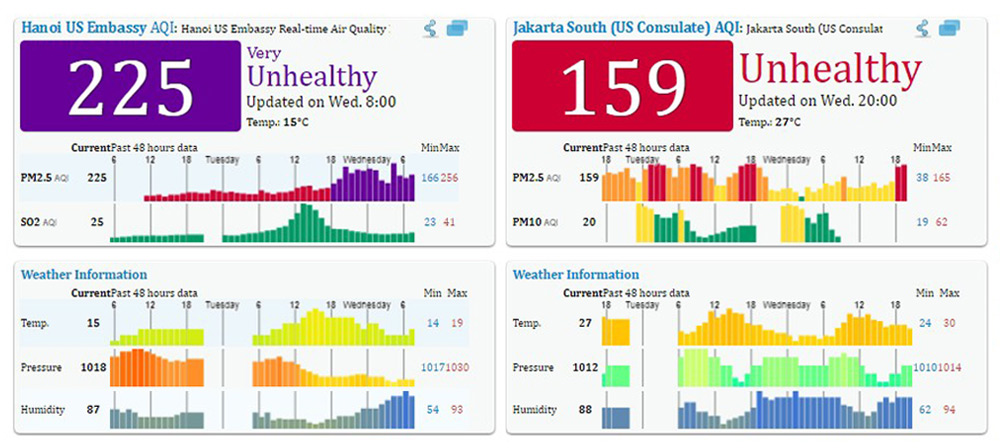
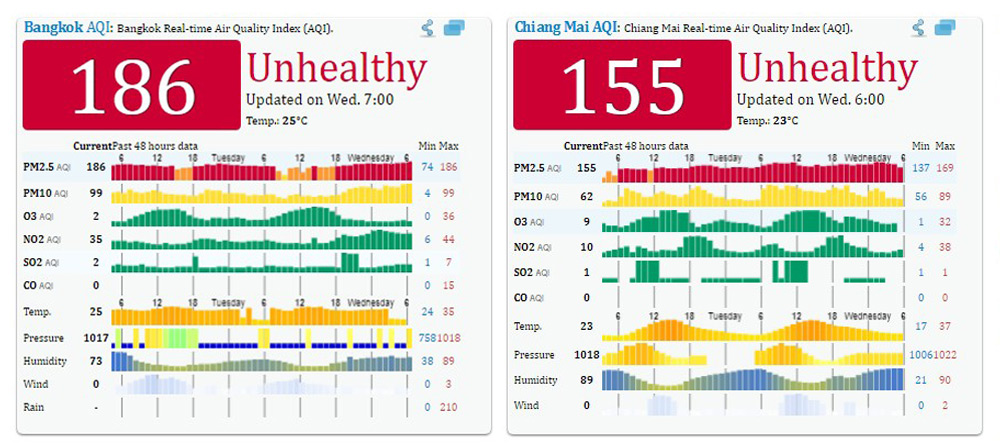
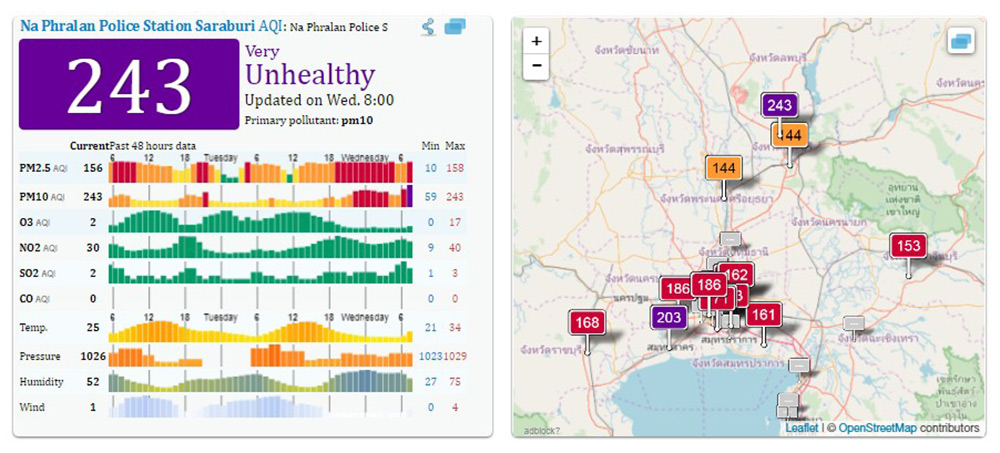
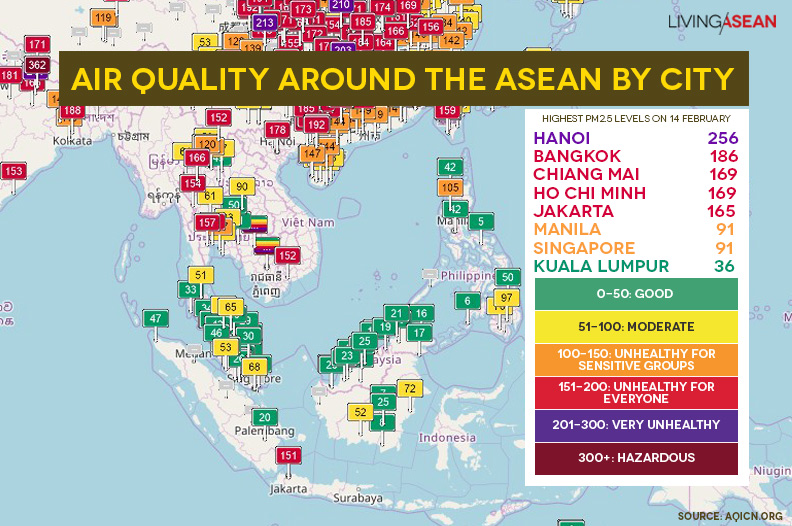
 Air Quality around the ASEAN
Air Quality around the ASEAN





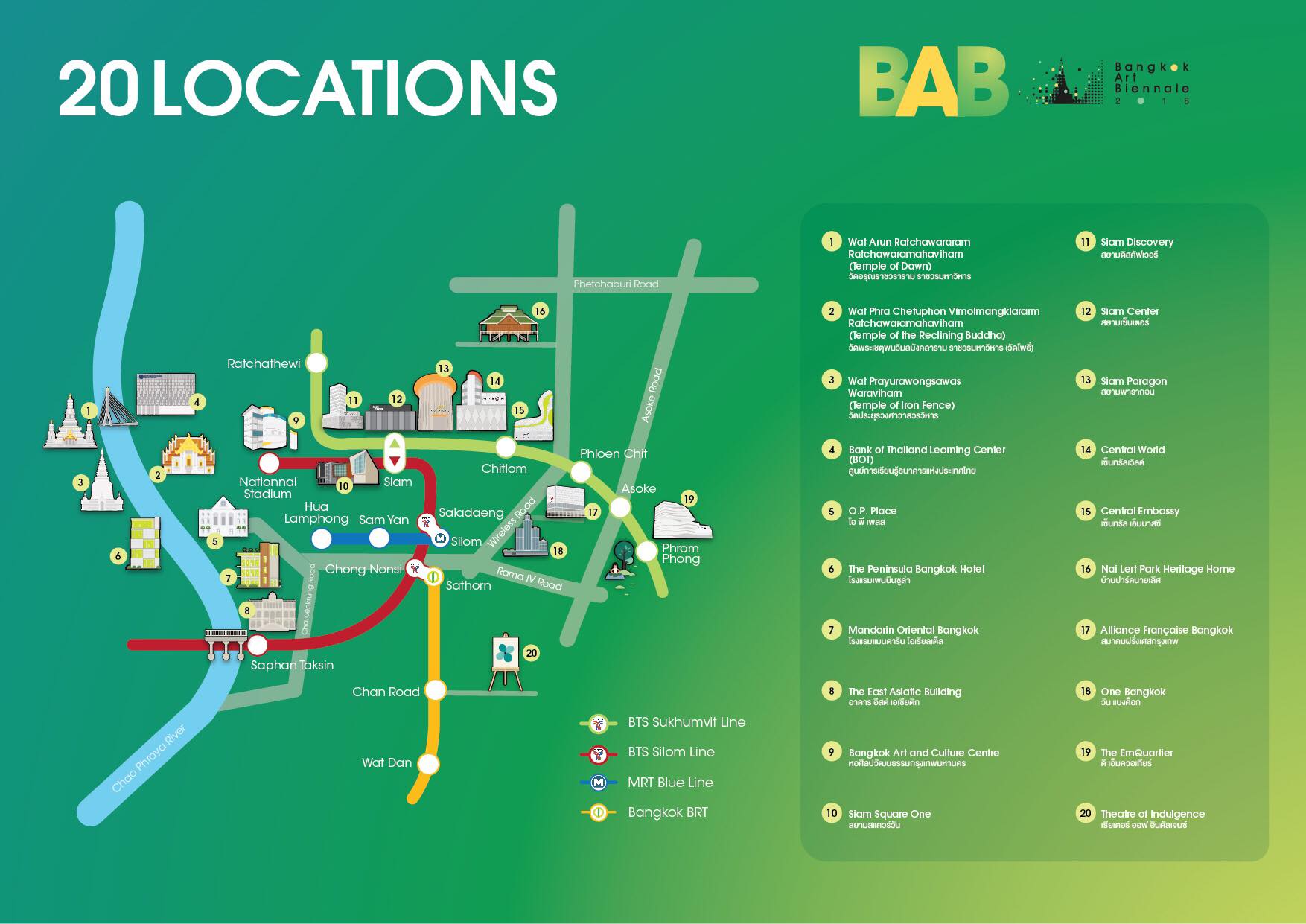
 Catching a Glimpse of War Memorials Across Southeast Asia
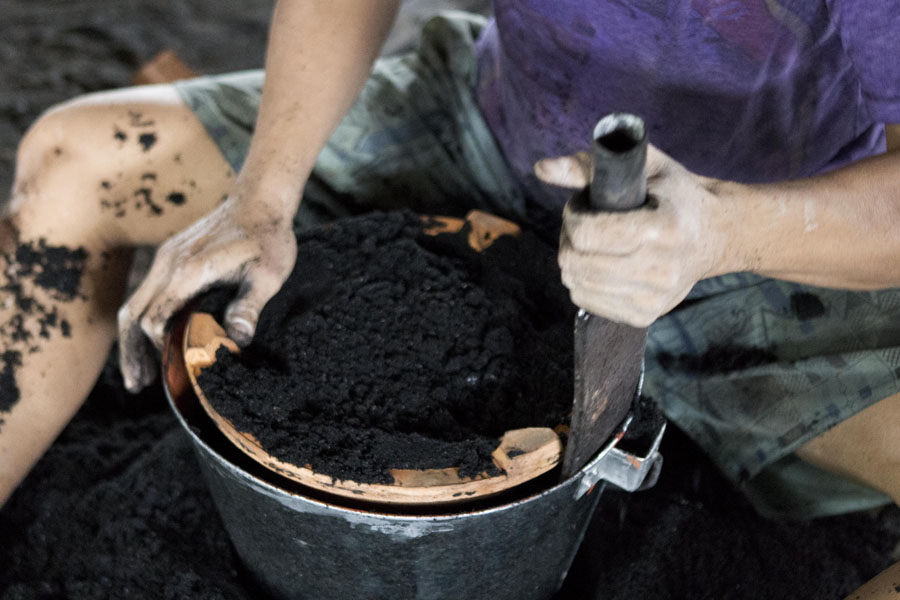
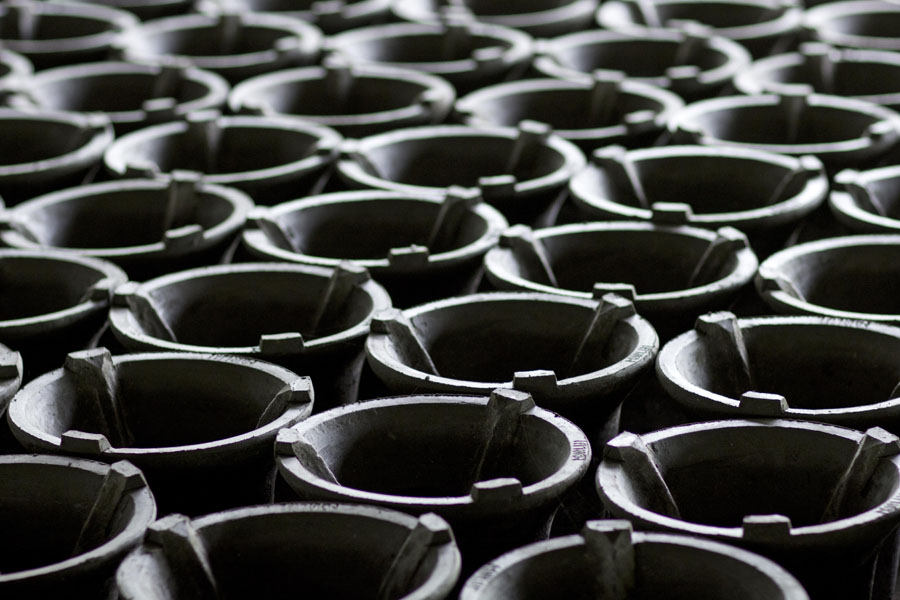
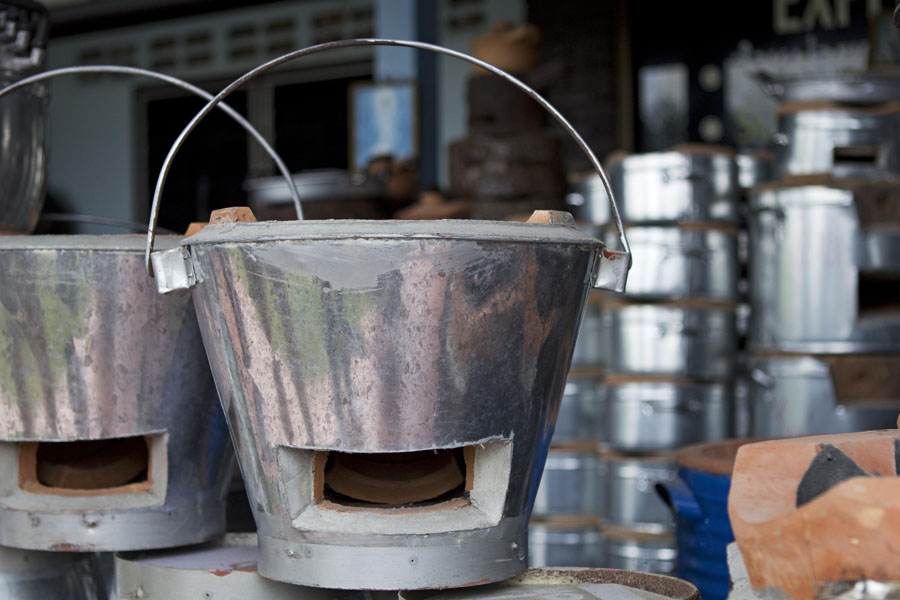
Catching a Glimpse of War Memorials Across Southeast Asia  The Making of the “Super Ung-Lo,” Ratchaburi’s Fuel-Efficient Cook Stove
The Making of the “Super Ung-Lo,” Ratchaburi’s Fuel-Efficient Cook Stove 









































 Refrain from touching materials on display
Refrain from touching materials on display Refrain from loud noises or running and playing within the building
Refrain from loud noises or running and playing within the building Refrain from bringing bags/gear into art exhibition areas
Refrain from bringing bags/gear into art exhibition areas Refrain from smoking or eating at in exhibition areas
Refrain from smoking or eating at in exhibition areas Keep an appropriate distance
Keep an appropriate distance Dress respectfully
Dress respectfully Always study the manual before attending an exhibition
Always study the manual before attending an exhibition